- Lansweeper Community
- Knowledge Center
- Knowledge Base
- Requirements
- vCenter scanning requirements
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Article History
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
on
08-27-2018
08:30 PM
- edited on
07-26-2023
08:17 PM
by
sophie
![]()
This page explains the scanning requirements needed to scan your VMware virtual environments using vCenter.
You can scan your VMware virtual environments using vCenter credentials. Scanning with vCenter gives a more complete overview of your virtual environment compared to the old VMware scanning method using the Managed Object Browser (MOB). Scanned vCenter data includes datacenters, datastores, clusters, ESXi hosts, VMware guests and more.
In order to scan your vCenter server, the requirements listed below must be met and you must set up a user with (at a minimum) read-only access to the vCenter server.
To make sure a vCenter server meets the requirements for scanning, do the following:
- Make sure that the machine is a vCenter Server Appliance (vCSA) and that TCP ports 135, 139 and 445 are closed on the vCenter server.
Scanning a vCenter Server environment installed as software on a Windows computer is not supported. If Lansweeper determines a machine to be a Windows computer, if it finds TCP port 135 to be open, vCenter scanning is skipped.
- Make sure TCP port 443 (HTTPS) is open on the vCenter server, as Lansweeper uses this port to determine whether the machine is a vCenter server.
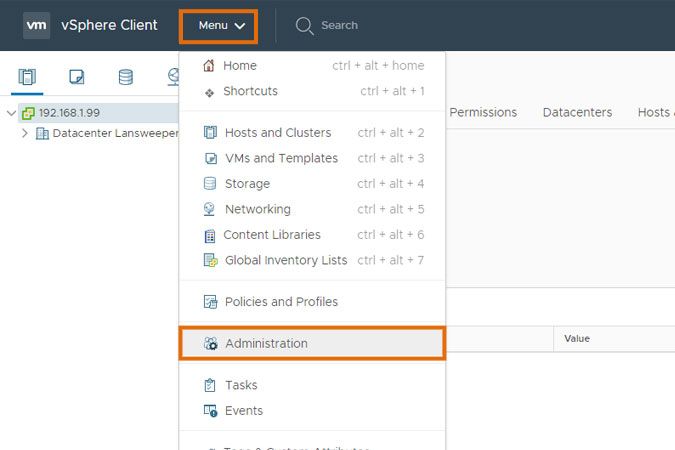
- Log into your vCenter server's vSphere Client.
- Select Administration from the dropdown menu.
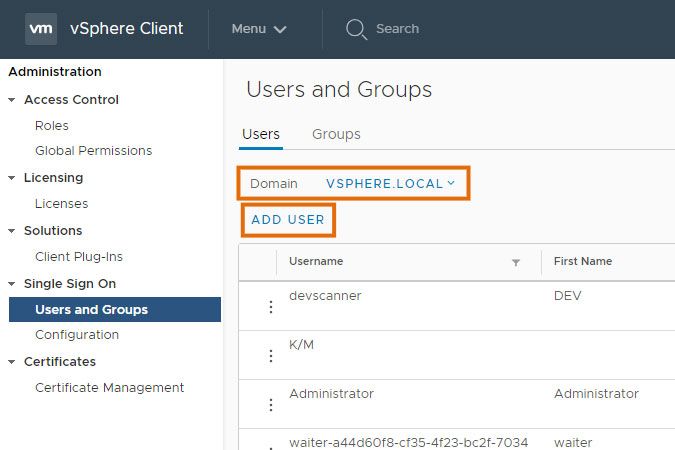
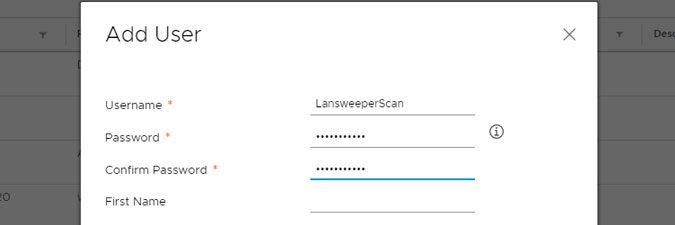
- Navigate to Users and Groups, select your preferred domain and select Add User.
- Enter your preferred credentials and click OK.
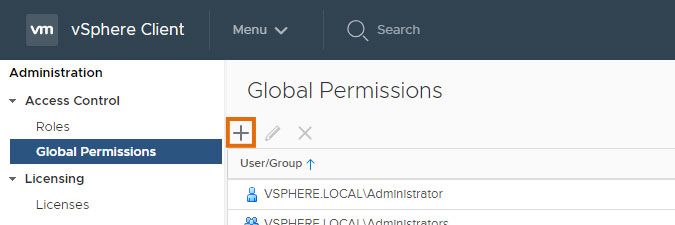
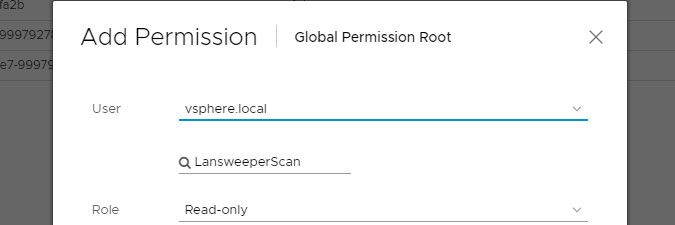
- Navigate to Global Permissions and select the "+" button.
- In the resulting pop-up, select the domain you created the user in earlier, enter the user, select Read-only and select OK.
- Your account should now be ready for use. You can test it by opening a web browser, browsing to the IP address of your vCenter server and submitting the username and password you created, which should grant you access to vCenter.
You can then start scanning the vCenter server by following the instructions in this knowledge base article.
Was this post helpful? Select Yes or No below!
Did you have a similar issue and a different solution? Or did you not find the information you needed? Create a post in our Community Forum for your fellow IT Heroes!
More questions? Browse our Quick Tech Solutions.
New to Lansweeper?
Try Lansweeper For Free
Experience Lansweeper with your own data. Sign up now for a 14-day free trial.
Try Now