- Lansweeper Community
- Knowledge Center
- Knowledge Base
- Cyber Security and Risk Insights
- Introduction to Vulnerability Risk Assessment
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
This documentation is for the old UI. For documentation for the new preview UI, Knowledge Base - Preview UI.
- Article History
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-14-2023 05:39 PM - edited 05-12-2025 11:06 AM
This page gives an overview of the Risk Insights module in Lansweeper, and explains how crucial some of the features are to maintain a secure system.
In today's interconnected world, understanding vulnerabilities is crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of systems and assets. Vulnerabilities represent weaknesses that malicious actors can exploit, potentially leading to unauthorized access, data breaches, or system disruptions.
In this article, we will delve into the world of vulnerabilities, exploring their sources, implications, and mitigation strategies.
- How Lansweeper identifies vulnerabilities
- Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
- Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)
- Exploitability
- Patch information
- Ignoring vulnerabilities
- Vulnerabilities in OT assets
How Lansweeper identifies vulnerabilities
Lansweeper uses CPE correlation to identify and map vulnerabilities to specific software, hardware, OS, or firmware products in your inventory.
Common Platform Enumeration (CPE) is a standardized naming system used to uniquely identify IT products. By assigning CPE identifiers to the components discovered in your environment, Lansweeper can match known vulnerabilities from external sources to your organization's products.
This matching process is powered by VulnCheck, which provides a curated and continuously updated vulnerability database.
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
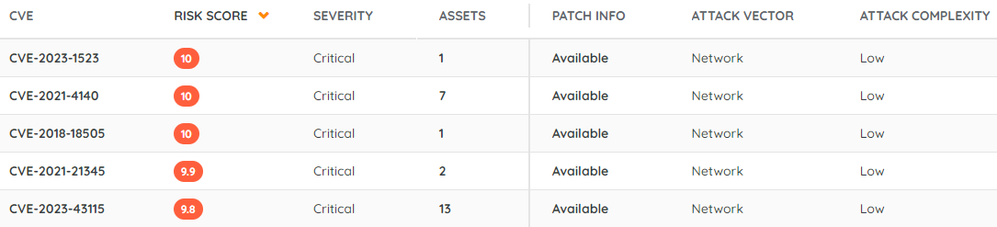
CVE, which stands for Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures, is an identification system used to uniquely identify vulnerabilities. Each CVE entry corresponds to a specific vulnerability and includes relevant details such as descriptions, impacts, and potential mitigations. By referencing CVEs, security professionals, researchers, and organizations can effectively communicate and track vulnerabilities across different systems and platforms.
To enrich its vulnerability information, Lansweeper uses VulnCheck as its primary provider for vulnerability intelligence data. VulnCheck in turn leverages information from NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology), CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency), MS (Microsoft), vendors and other databases. These sources provide valuable insights into known vulnerabilities, their impacts, and recommended mitigation measures. By utilizing information from these databases, Lansweeper ensures that it stays up-to-date with the latest vulnerabilities and security advisories.
The base score is a widely adopted industry-standard metric known as CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System). It allows for the comparison of vulnerabilities for prioritisation purposes. The base score ranges from 0 to 10, with a higher score indicating a more severe vulnerability.
Severity, derived from the base score, classifies vulnerabilities into four categories: low, medium, high, and critical. This classification enables organizations to prioritize their vulnerability management efforts and allocate resources accordingly.
The confidence level depicts the accuracy of vulnerability correlation. The confidence level can be categorized as either "Low" or "High." A high confidence level indicates a high degree of certainty that the vulnerability has been correctly identified and correlated, while a low confidence level implies a lesser degree of certainty. This additional information helps users gauge the reliability and credibility of vulnerability findings. For a more detailed overview of this feature, have a look at the Confidence level article.
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)
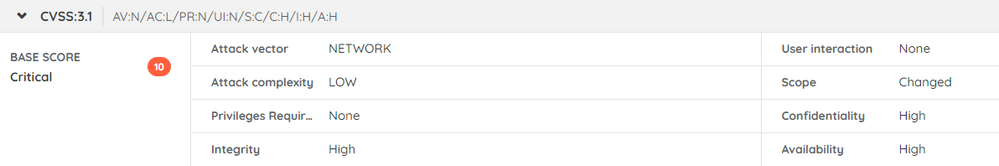
Attack vector
The attack vector describes the context or path through which a vulnerability can be exploited. It provides insights into how an attacker can gain access to a system or network. The possible values for the attack vector include:
- Network: Vulnerabilities with this rating are remotely exploitable, either from one or more hops away or over the internet.
- Adjacent: A vulnerability with this rating requires network adjacency for exploitation, meaning the attack must originate from the same physical or logical network.
- Local: Vulnerabilities with this rating are not exploitable over a network. The attacker must have local access to the system or employ remote access protocols like SSH or RDP. Social engineering techniques may also be used to trick unsuspecting users into initiating the exploit.
- Physical: In this type of attack, the adversary must physically interact with the target system to exploit the vulnerability.
Attack complexity
The attack complexity describes the level of difficulty involved in successfully exploiting a vulnerability. It assesses the ease or complexity of launching an attack using the vulnerability and can be categorized as either "Low" or "High".
Privilege
Privilege describes the level of privilege or access an attacker requires to successfully use a vulnerability. The level of privilege can be categorized as:
- None: There are no privileges required to abuse a vulnerability.
- Low: A limited amount of privileges are required to abuse a vulnerability.
- High: A high amount of privileges are required to abuse a vulnerability.
Integrity
Integrity refers to the impact on the integrity of information resulting from the successful use of a vulnerability. It evaluates the potential tampering or modification of data and can be categorized as follows:
- None: There is no loss of integrity of any information.
- Low: A limited amount of information might be tampered with or modified, but there is no serious impact on the protected system.
- High: The attacker can modify any/all information on the target system, resulting in a complete loss of integrity.
User interaction
User interaction refers to whether a user, other than the attacker, needs to perform an action for the successful exploitation of a vulnerability. User interaction can be categorized as follows:
- None: No user interaction is required for the vulnerability to be exploited.
- Required: A user must complete specific steps or actions for the exploit to succeed. For example, the user might be prompted to install certain software or perform an action that aids the attacker.
Scope
The scope of a vulnerability indicates whether its exploitation extends beyond the initially compromised system (Changed) or remains confined to the originally vulnerable component (Unchanged).
Confidentiality
Confidentiality measures the impact on the confidentiality of information resulting from the successful use of a vulnerability. It evaluates the potential exposure of sensitive data and can be classified into the following categories:
- None: There is no loss of confidentiality.
- Low: The vulnerability might result in limited or intermittent impact on the confidentiality of information.
- High: The successful exploitation of the vulnerability leads to a complete loss of confidentiality of the impacted system or information.
Availability
Availability impact measures the impact on system availability resulting from the successful use of a vulnerability. It assesses the potential disruption or loss of service and can be classified into the following categories:
- None: There is no loss of availability.
- Low: Availability might be intermittently limited, or the performance might be negatively impacted as a result of a successful attack.
- High: There is a complete loss of availability of the impacted system or information.
Exploitability
Exploitability refers to how easily an attacker can take advantage of a vulnerability. Understanding exploitability is crucial for developing effective mitigation plans based on vulnerability information.
To find out more about the information Lansweeper provides on exploitability, check out Understanding exploitability fields.
Patch information
The patch info column provides critical information about the availability of patches to address identified vulnerabilities. It assists users in prioritizing their remediation efforts by categorizing the patch status into two states: "Available" or "Unknown."
- Available: If the patch status is marked as "Available", users can go into the vulnerability to access links to download and install the necessary patches, offering users a direct path to mitigate the vulnerability.
- Unknown: If the patch status is marked as "Unknown", it signifies that the availability of patches is currently not determined or disclosed. Users should actively monitor for updates from security authorities to stay informed about patch releases.
Ignore assets and vulnerabilities
Although vulnerabilities pose potential risks, there may be situations where users may choose to ignore them. Lansweeper acknowledges that different circumstances may warrant such decisions and provides users with options to justify ignoring a vulnerability. The available reasons for ignoring vulnerabilities include:
- False positive: When Lansweeper identifies a vulnerability incorrectly, considering it a false positive, users can choose to ignore it.
- Risk accepted: In certain cases, organizations may consciously accept the risks associated with a vulnerability due to specific mitigating factors or alternative security measures.
- Not relevant: If a vulnerability is deemed irrelevant to an organization's systems, applications, or infrastructure, it can be ignored.
For more information, see our article on how to take advantage of the ignore feature.
Vulnerabilities in OT assets
If you have linked your OT Hub with Lansweeper Sites, you can also view vulnerability information related to your OT assets. OT assets and IT assets are managed within the Risk Insights module.
To view a list of vulnerabilities affecting your OT assets:
- Go to your Lansweeper Site.
- Go to Risk Insights > Active vulnerabilities, and select Advanced filter view.
- Add a new filter.
- Select Asset type, Equal to, and enter OT.
- Select Apply.
Check out our overview of OT asset management features to learn more.
New to Lansweeper?
Try Lansweeper For Free
Experience Lansweeper with your own data. Sign up now for a 14-day free trial.
Try Now
