- Lansweeper Community
- Knowledge Center
- Knowledge Base
- Scanning your network
- How to scan a Windows computer
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Article History
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
on
03-08-2015
07:30 PM
- edited on
10-04-2024
11:22 AM
by
Nils
![]()
This page explains how you can use Lansweeper to scan a Windows computer, by either using a scanning agent or setting up scanning targets.
There are two main ways you can scan a Windows domain or workgroup computer: using a scanning agent or without using a scanning agent.
You can use any of the following scan types to scan a new Windows computer that hasn't been scanned before: Active Directory Computer Path, Active Directory Domain, IP Range, Windows Computer, or Workgroup.
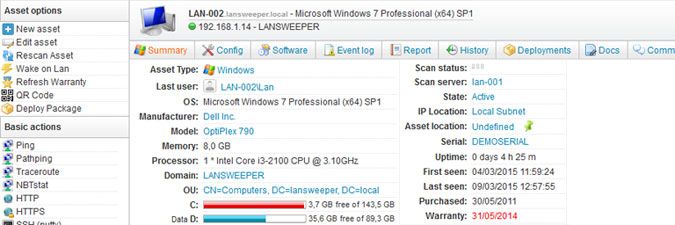
Regardless of the scan type, the collected Windows data includes information about disks, event log entries, installed updates, logged-in users, manufacturer, model, memory, monitors, motherboard, network cards, operating system, processor, services, software, license keys, uptime, and more!
Scan a Windows computer without a scanning agent
To scan a Windows domain or workgroup computer without a scanning agent:
- Make sure you meet the Windows domain or workgroup scanning requirements.
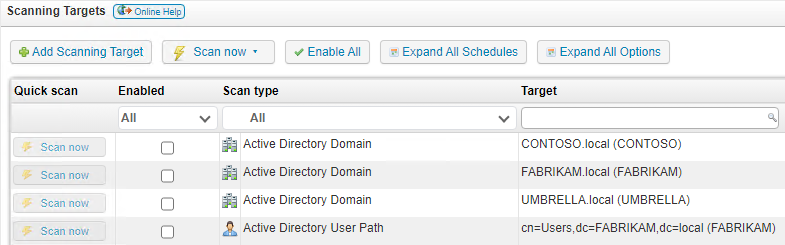
- In your web console, go to Scanning > Scanning targets, and select Add Scanning Target.
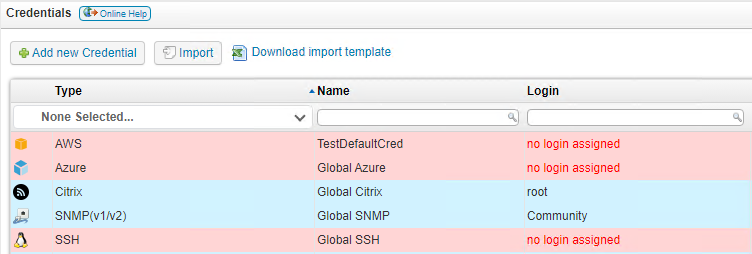
If you have multiple scanning servers, there will be a separate configuration tab for each server. - Go to Scanning > Scanning credentials, and select Add new Credential.
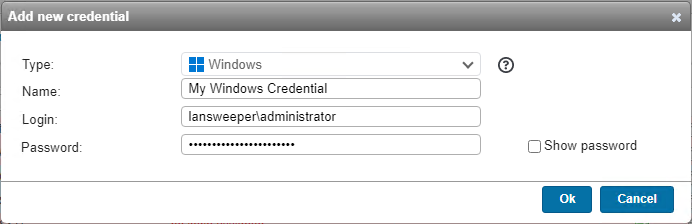
- In the popup, select Windows as the Type, and enter your Windows username and password.
- For domain credentials, submit a down-level logon name like NetBIOS domain name\username or a user principal name (UPN) like username@yourdomain.local.
- For local credentials, use the format
.\username. - Microsoft accounts like username@outlook.com can be used as credentials as well.
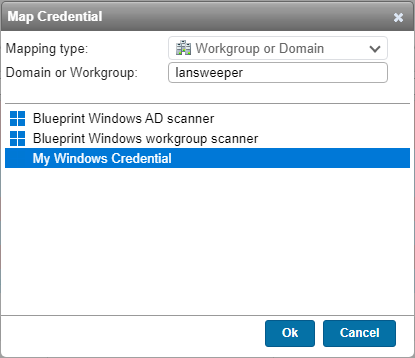
You can use the same username and password for all Windows computers by editing the global Windows credential. - If the credential you set up is not a global credential, you will need to map the credential to your computer's domain/workgroup, name, IP address or IP range.
In the Credential Mapping section of the Scanning credentials page, select Map Credential. - Select your preferred Mapping type, and enter the required information.
- Select your Windows credential, and Ok.
- Wait for your scanning schedules to trigger or initiate an immediate scan by selecting Scan now next to the scan target under Scanning > Scanning Targets.
You can monitor the progress of your scan request under Scanning > Scanning Queue.
Scan a Windows computer with a scanning agent
There are separate articles on how to scan Windows computers with the LsAgent or LsPush scanning agent.
The scanning agents scan largely the same data as agentless scanning methods, but have several important advantages:
- Scanning agents are immune to almost all scanning errors, including access denied and firewall errors.
- Scanning agents allow you to scan the computers of remote workers.
- Scanning agents generate a lot less traffic during scanning.
- Scanning agents can scan Home editions of Windows.
- Scanning agents do not require administrative privileges.
New to Lansweeper?
Try Lansweeper For Free
Experience Lansweeper with your own data. Sign up now for a 14-day free trial.
Try Now