- Lansweeper Community
- Knowledge Center
- Knowledge Base
- Requirements
- Introduction to the SQL LocalDB database server
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Article History
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
on
11-25-2019
07:30 PM
- edited on
08-04-2023
02:00 PM
by
Nils
![]()
From Lansweeper 7.2 onward, SQL LocalDB is one of the available database server options for hosting your Lansweeper database. The LocalDB option is a custom variant of Microsoft SQL Server 2014 Express. It was introduced into Lansweeper as a replacement for the deprecated Microsoft SQL Compact database server.
This knowledge base article provides further information on what LocalDB is, why it was introduced, how to manage it and how to convert from or to this database server.
What is LocalDB?
Lansweeper's LocalDB database server option is based on SQL Server 2014 Express. It has many of the same properties as SQL Server but also some notable differences.
SQL Server 2014 was used as the basis for Lansweeper's LocalDB implementation as it is compatible with a wide range of operating systems and architectures. Below is a comparison between Lansweeper's different database server options.
| Database server | Packaged with Lansweeper | Max database size | Support for distributed Lansweeper components | Support for multiple scanning servers | Lansweeper support status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SQL Compact | ✔ | 4 GB | ✘ | ✘ | unsupported from March 2020 onward |
| SQL LocalDB | ✔ | 10 GB | ✘ | ✘ | supported database server |
| SQL Server | ✘ (manual install required prior to installing Lansweeper) |
|
✔ | ✔ | supported database server |
Why was this new database server option introduced?
LocalDB was introduced primarily as a replacement for the deprecated Microsoft SQL Compact database server option. Both database servers come packaged with the Lansweeper installer and are therefore easy to use. However, SQL Compact was phased out by March 2020 for multiple reasons:
- SQL Compact has a number of limitations in functionality and reporting that make it incompatible with future Lansweeper features.
- SQL Compact has a 4 GB database size limit.
- SQL Compact has limited performance in large networks.
- SQL Compact is fundamentally different from SQL Server, requiring separate development. As SQL LocalDB and SQL Server are basically the same database engine, dropping SQL Compact allows for Lansweeper development to be streamlined.
- SQL Compact has been deprecated by Microsoft and support will be discontinued.
How to manage your Lansweeper LocalDB database
Lansweeper tools like DatabaseMaintenance.exe and ConfigEditor.exe can be used to perform certain operations on your LocalDB instance, as is the case for other database servers. For instance, you can change the LocalDB database password in the same way as you would change a SQL Server password.
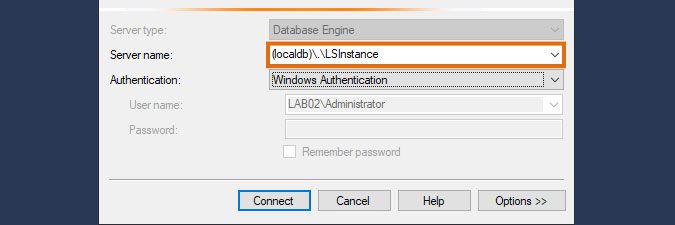
In addition, you can connect to your LocalDB instance using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), though only locally from your Lansweeper server. The following users have access to your LocalDB instance by default:
- The Windows user that performed the Lansweeper installation.
- The SQL user lansweeperuser, which is generated during the Lansweeper installation.
Your SQL instance name under LocalDB is (localdb)\.\LSInstance. Using this server name and one of the two user accounts listed above, you can access your Lansweeper database using SSMS.
Which migration paths are available from and to LocalDB?
You can convert a SQL Compact database to LocalDB. You can also convert a LocalDB database to SQL Server, if you require the added SQL Server functionality. It's theoretically possible to migrate from SQL Server 2014 or older to LocalDB as well, though we would not recommend this, as a full SQL Server instance offers more functionality.
Automatically migrating from Compact to LocalDB
If your Lansweeper installation is on version 7.2.107.4 or lower and hosted in the Compact database server, you can easily convert your database by following these update instructions. During the Lansweeper update process, your database is converted to LocalDB. This process is automatic and requires no user input.
Manually migrating from Compact to LocalDB
If your Lansweeper installation is on version 7.2.108.6 or if you only have a SQL Compact lansweeperdb.sdf file and not a full Lansweeper installation, you will need to manually convert your database.
Migrating from LocalDB to SQL Server
There are various reasons why you might choose to move from LocalDB to SQL Server:
- Spread your Lansweeper components over multiple servers
- Add more scanning servers to your Lansweeper installation
- Increase your database capacity by using a paid SQL Server edition
- Connect to your database remotely to perform remote queries
If required, you can move from LocalDB to a full SQL Server 2014 or newer, any edition.
Was this post helpful? Select Yes or No below!
Did you have a similar issue and a different solution? Or did you not find the information you needed? Create a post in our Community Forum for your fellow IT Heroes!
More questions? Browse our Quick Tech Solutions.
New to Lansweeper?
Try Lansweeper For Free
Experience Lansweeper with your own data. Sign up now for a 14-day free trial.
Try Now