- Lansweeper Community
- Knowledge Center
- Knowledge Base
- Scanning your network
- Scan a network device
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Article History
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
on
03-03-2015
07:30 PM
- edited on
02-01-2024
11:08 AM
by
Nils
![]()
This page explains how Lansweeper can scan network devices, such as cameras, firewalls, printers, routers, and switches.
Apart from scanning Linux, Unix, Mac and Windows computers, as well as VMware servers, Lansweeper is also capable of scanning network devices. Some examples of network devices are: cameras, firewalls, mail servers, music systems, NAS devices, printers, routers, switches, UPS devices, VOIP phones and web servers.
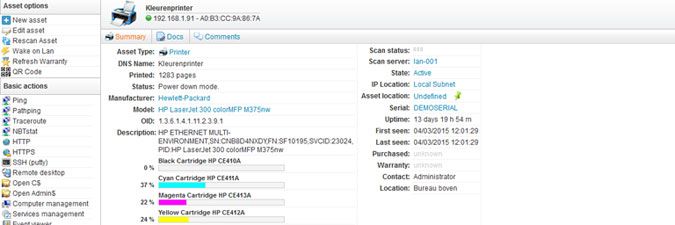
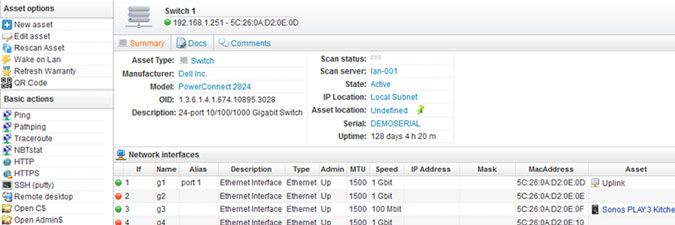
The exact data returned depends on the protocols enabled on the device, as well as the device type. Below are two sample device pages, one of a printer and one of a switch.
Scanned printer data includes device description, network interfaces, manufacturer, model, printed pages, printer status, toner levels, serial number, uptime and more.
Scanned switch data includes device description, manufacturer, model, port mapping information, serial number, uptime and more.
Scan a network device
- Make sure you meet the network device scanning requirements.
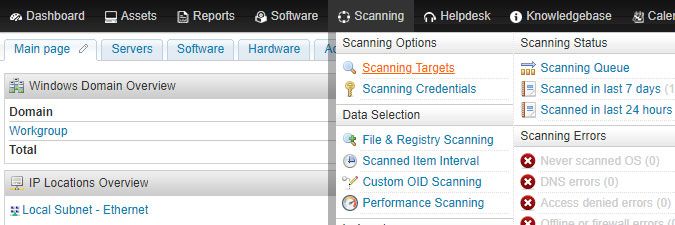
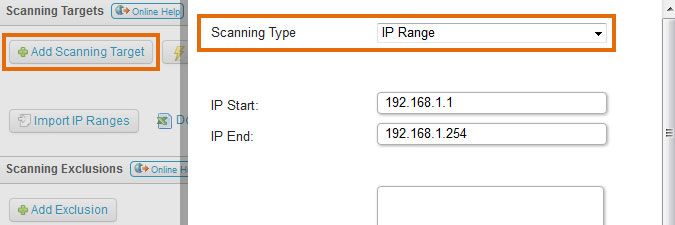
- Submit your device's IP range for scanning by selecting Add Scanning Target in the Scanning > Scanning Targets section of the web console.
If you have multiple scanning servers, there will be a separate configuration tab for each server. When submitting your range, you will be asked to specify a scanning schedule. If your device uses a custom SIP or SSH port, make sure to submit the correct port number as well.
If the Save Pinged IP option is ticked, which it is by default in recent Lansweeper releases, assets are generated for all IP addresses that respond to a ping request.
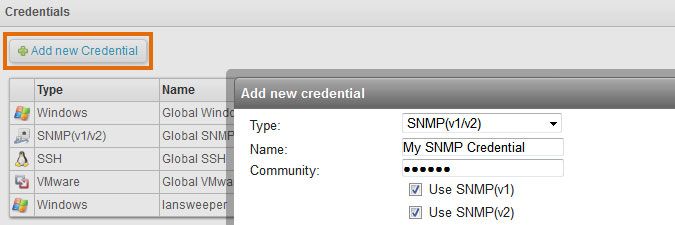
If Save Pinged IP is not ticked, an asset is only generated for a network device if data can be pulled from one or more of the following protocols on the device: Bonjour, DNS-SD, FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, JetDirect, mDNS, SIP, SMTP, SNMP (SNMPv1, SNMPv2 or SNMPv3), SSDP, SSH, Telnet, UPnP or WMI. - If your device supports SNMP or SSH, submit your SNMP/SSH credential in the Scanning > Scanning Credentials section of the web console.
You can use the same credential for all SNMP/SSH enabled devices by editing the Global SNMP/SSH credential or submit a non-global credential with the Add new Credential button.
SNMPv1, SNMPv2 and SNMPv3 are supported.
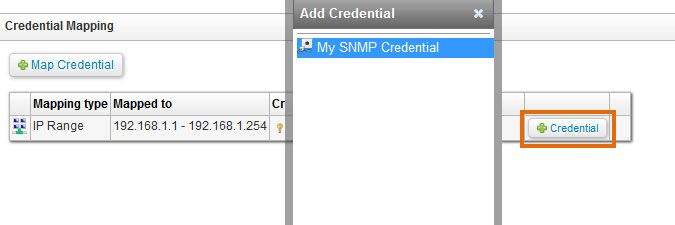
Keep in mind that SSH scanning is only supported for *nix based systems like Linux, Unix and Mac computers. Ideally, other network devices are scanned through SNMP. We have scanning requirements for Linux/Unix and Mac. - If the credential you set up is not a global credential, map the credential to your device's IP range by selecting + Credential for the range.
- Wait for your scanning schedules to trigger or initiate an immediate scan by selecting Scan now next to the range under Scanning > Scanning Targets.
- Monitor the progress of your scan request under Scanning > Scanning Queue.
New to Lansweeper?
Try Lansweeper For Free
Experience Lansweeper with your own data. Sign up now for a 14-day free trial.
Try Now