This website uses cookies. By clicking Accept, you consent to the use of cookies. Click Here to learn more about how we use cookies.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
- Lansweeper Community
- Knowledge Center
- Knowledge Base
- Troubleshooting Scanning Issues
- Linux scanning error: LinuxNoSudoRights
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Lansweeper
Champion Sweeper
Options
- Article History
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
01-03-2013 07:30 PM - edited 06-05-2024 09:22 AM
If your scanning credential does not have the sudo rights to scan the required Linux information, you may receive a LinuxNoSudoRights error during a Linux scan.
Different Linux distributions may require different configuration commands.
To resolve the Linux scanning error:
- Navigate to your Linux Terminal.
- If necessary, create a new group by running
sudo groupadd groupname, replacinggroupnamewith your preferred group name: - Add a user to the group by running
sudo usermod -a -G groupname username, wheregroupnameandusernameare replaced by your desired names: - Ensure your user has been added to your group by running
grep groupname /etc/group. - Enter
sudo visudoand a password, if prompted. - To give an individual user permission to use sudo, use the arrow keys to navigate through the file and locate a line that looks
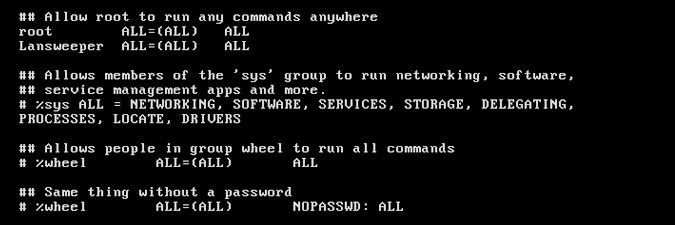
username ALL=(ALL) ALL. To give all users within a group permission to use sudo, locate a line that looks like%groupname ALL=(ALL) ALL. Note the "%" before the group name. Common groups with sudo rights are sudo and wheel. - Select i to enter insert mode. Use the arrow keys to move the cursor and click Enter to insert a new line. Do not remove existing lines from the file. Instead, add "#" to the start of a line to ignore that line. This way no information is mistakenly deleted.
- Add a line for each additional user or group you want to grant sudo rights to. Use the same format as the users and groups already in the file. In the example below, we gave sudo rights to a user called Lansweeper.
- When you are done editing the file, click Escape to exit insert mode.
- Type
:wqthen click Enter to save and exit the editor. - Navigate to the Lansweeper web console and rescan the client machine with the user account you granted sudo rights to.
The LinuxNoSudoRights errors should now be resolved. If the issue persists, browse and post in our Community Forum, or contact our support team directly.
New to Lansweeper?
Try Lansweeper For Free
Experience Lansweeper with your own data. Sign up now for a 14-day free trial.
Try Now